J20.9: Acute bronchitis, unspecified
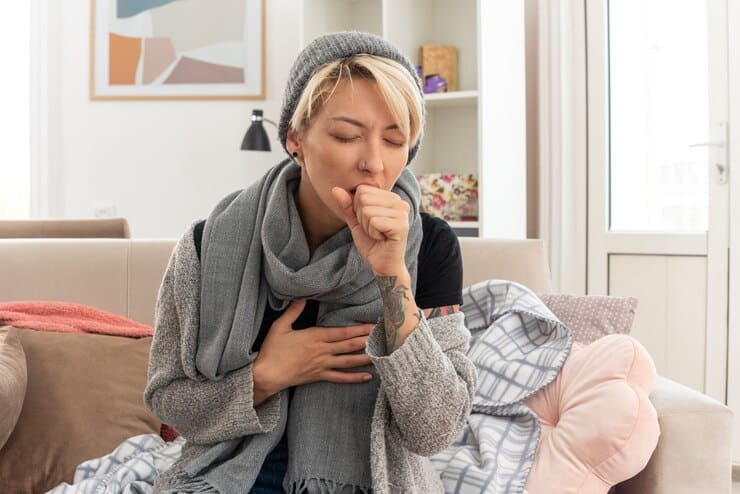

When it comes to medical billing for respiratory conditions, one common scenario is coding for acute bronchitis. Often, medical professionals encounter cases where acute bronchitis is the primary diagnosis, yet specific details are lacking.
In these instances, the Acute Bronchitis ICD-10 code J20.9 becomes crucial. This code, designated for acute bronchitis, is unspecified.
J20.9 is essential for providers and medical billers alike. It represents cases where the diagnosis of acute bronchitis is clear, but the specifics are not detailed. Utilizing this code correctly helps maintain clarity in medical records, simplifying the billing process.
In this blog, we will shed light on bronchitis, and its main types. after this, we will only explore acute bronchitis, its types and sub-types, tips to overcome acute bronchitis, treatment, and diagnosis.
What is bronchitis?
Bronchitis, a common respiratory condition, often surfaces in clinical discussions and medical billing contexts, particularly with its specific ICD 10 code, J40. This ailment involves inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that connect the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs.
As these tubes swell and produce mucus, breathing becomes harder, leading to a persistent cough and other discomforts.
Varieties of bronchitis?
here are two primary types of bronchitis: acute and chronic.
Acute bronchitis typically develops from a cold or other respiratory infection and is relatively short-term.
Chronic bronchitis, a more severe form, is characterized by persistent irritation or inflammation of the bronchial tubes, often due to smoking, and is part of a group of lung diseases known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Knowing the different kinds of bronchitis, which are labeled as J20.9 in the Bronchitis ICD 10 system, is key for proper and effective treatment. The main two types of bronchitis are:
- Acute Bronchitis
- Chronic Bronchitis
Define Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis, known in the medical billing world by its ICD-10 code, J20.9, is a common respiratory condition. It involves the inflammation of the bronchi, the major air passages to the lungs.
This condition often develops from a cold or other respiratory infection and presents symptoms like coughing and shortness of breath. The J20.9 code is not just a number; it’s key to effective healthcare delivery and seamless medical billing processes.
Recognizing the Signs of Acute Bronchitis
Cough: It’s usually dry at first but can produce mucus as it progresses.it may last for 10 to 20 days.
Mucus Production: As the bronchial tubes inflame, they produce mucus. This can be clear, white, yellow, or green. Note that the color does not necessarily indicate a bacterial infection.
Fatigue: Acute bronchitis can make you feel unusually tired and drained. This is your body’s response to fighting the infection and the extra effort it takes to breathe.
Shortness of Breath: Inflammation and mucus in the bronchial tubes make it harder to breathe, leading to feelings of breathlessness, especially with physical activity.
Mild Fever: A low-grade fever usually accompanies acute bronchitis, signaling your body’s fight against infection
Chest Discomfort: Coughing and inflammation can cause chest tightness and soreness, which might feel worse when coughing or taking deep breaths.
Different Forms of Acute Bronchitis with their ICD-10 Codes?
In medical coding, acute bronchitis is categorized into different types depending on what causes it. Below are several kinds of acute bronchitis and the ICD-10 codes used for them.
1:Acute Viral Bronchitis
Acute viral bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs, primarily caused by a virus. It typically manifests as a persistent cough, often accompanied by other cold symptoms.
It is further classified into different types and it is recommended to use the specific code.
Acute Bronchitis due to Coxsackievirus
This condition develops from an infection with the Coxsackievirus. For diagnosing this specific type, utilize code J20.3.
Acute Bronchitis due to Parainfluenza Virus
This form of bronchitis is caused by the Parainfluenza virus. Use the code J20.4 for its accurate medical diagnosis.
Acute Bronchitis due to Respiratory Syncytial Virus
The Respiratory syncytial virus is the cause of this bronchitis variant. Diagnosis is made using code J20.5.
Acute Bronchitis due to Rhinovirus
Rhinovirus infection leads to this type of acute bronchitis. Code J20.6 should be applied to diagnose it.
Acute Bronchitis due to Echovirus
This type is caused by an Echovirus infection.
For diagnosis, refer to code J20.7.
2: Acute Bronchitis with Bronchospasm
This type is like bronchitis with an added twist – bronchospasm. Imagine the airways being squeezed by tiny muscle spasms, leading to coughs and a struggle to breathe. It’s bronchitis plus a little extra challenge.
In the world of ICD-10 codes, J20.9 is the star for acute bronchitis with bronchospasm.
3: Acute Bacterial Bronchitis
Type of bronchitis where bacteria are the culprits. Those affected might experience a cough that brings up the mucus, a sense of discomfort in the chest, and sometimes, a fever that just won’t quit.
J20.8 That’s the code you’ll need for cases when Acute bronchitis is due to other specified organisms.
Acute Bronchitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae
This type of acute bronchitis comes from the Mycoplasma pneumoniae bacteria.
Use J20.0 to identify this particular cause of acute bronchitis when diagnosing and billing.
Acute Bronchitis due to Hemophilus influenzae
This specific kind of acute bronchitis is caused by the Hemophilus influenzae bacteria.
When this is the cause, the ICD-10 code J20.1 is used for accurate diagnosis and billing.
Acute Bronchitis due to Streptococcus
When acute bronchitis is due to Streptococcus bacteria, it’s this specific type.
For cases like this, J20.2 is the ICD-10 code utilized for proper diagnosis and billing.
4:Acute Asthmatic Bronchitis
Think of this as bronchitis mixed with asthma. It usually causes coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, often after something triggers the asthma.
Use the code J45.9. This code helps in medical billing to clearly identify cases of bronchitis that also involve asthma, ensuring accurate treatment and billing.
Approaches to Diagnosing and Treating Acute Bronchitis
Diagnosis of Acute Bronchitis
Diagnosing acute bronchitis accurately is key in the medical field. Doctors typically start with a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination to identify characteristic symptoms like a persistent cough.
To exclude other lung conditions, such as pneumonia, a chest X-ray might be recommended. Further, laboratory tests, including blood tests and sputum analysis, can be crucial.
These tests help in confirming the diagnosis, allowing for precise coding for medical billing, with the J20.9 diagnosis code being commonly used for acute bronchitis.
Treatment of Acute Bronchitis
The treatment approach for acute bronchitis primarily focuses on symptom relief, as the condition is often viral and does not respond to antibiotics. Medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce airway inflammation and ease breathing difficulties.
Inhaled steroids and expectorants can also be beneficial. Home remedies, including steam inhalation and increased fluid intake, are often advised to alleviate symptoms. Crucially, patients are urged to avoid smoking, as it can exacerbate the condition. Throughout the treatment process, accurate use of the diagnosis code for acute bronchitis, J20.9, ensures that medical billing is precise.
Strategies for Avoiding Acute Bronchitis
Prioritize Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing helps reduce the risk of viral infections leading to bronchitis.
Get Vaccinated: Stay updated with flu shots and pneumonia vaccines to lower bronchitis risk.
Avoid Tobacco Smoke: Smoking cessation and avoiding secondhand smoke can significantly decrease bronchitis chances.
Use Masks in Polluted Areas: Wearing masks in dusty or polluted environments helps protect your respiratory system.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet and regular exercise strengthen the immune system against infections.
Keep Indoor Air Clean: Use air purifiers and avoid indoor pollutants to reduce respiratory irritants.
Manage Chronic Conditions: Effectively controlling asthma or allergies reduces the likelihood of developing bronchitis.
Final thoughts
Acute bronchitis and its corresponding ICD-10 code, J20.9, is crucial for effective diagnosis and billing in healthcare. This knowledge ensures precise treatment and enhances patient care. Remember, J20.9 isn’t just a code; it’s a gateway to better healthcare management.
By familiarizing ourselves with J20.9 and related aspects, we contribute to a more efficient and accurate medical system, ultimately benefiting both providers and patients. Stay informed, and stay ahead in the world of medical billing and patient care.